Definition of Learning Disabilities
The terms learning disability, dyslexia, reading disability, and perceptual problems are frequently used in place of one other by the lay public.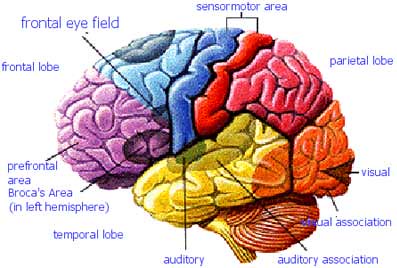
Learning disability is a more general term and refers to a difficulty in any aspect of learning, rather than merely the inability to read (dyslexia specifically).
Description of Learning Disabilities
Learning disabilities are generally divided into two groups: Primary (inherited) and Secondary (caused by a physical factor that interferes with learning as a result of a brain injury.)
The most common learning disabilities fall into five, general categories:
1. Dyslexia is a disorder in which there is difficulty understanding written words.
2. Dysgraphia involves difficulty in writing words or writing within a defined space.
3. Auditory and Visual Processing Disorders involve sensory proccessing disabilities within the brain, resulting in difficulty understanding language.
4. Dyscalculia involves an inability to understand and perform mathmetical processes, especially simple calculations.
5. Visuo-spacial motor and memory disorders involve a wide variety of non-verbal learning and memory functions including processing, evaluating and organizing perceived data.