It seems like you might be looking for ways to enhance user accessibility, user interface (UI), and user experience (UX) to increase your user base. Here are some strategies to achieve this:
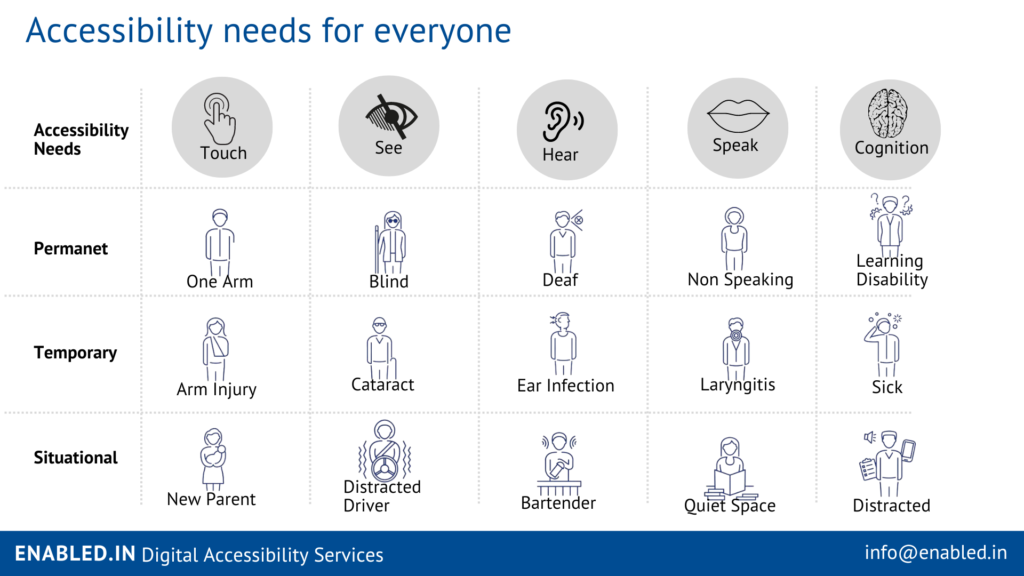
| Accessibility Needs | Touch | See | Hear | Speak | Cognition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permanet | One Arm | Blind | Deaf | Non Speaking | Learning Disability |
| Temporary | Arm Injury | Cataract | Ear Infection | Laryngitis | Sick |
| Situational | New Parent | Distracted Driver | Bartender | Quiet Space | Distracted |
User Accessibility:
- Adopt Inclusive Design: Ensure that your UI/UX design considers diverse user needs, including those with disabilities.
- Alt Text for Images: Provide descriptive text for images to assist visually impaired users who use screen readers.
- Keyboard Navigation: Ensure all interactive elements can be accessed and used via keyboard for users who cannot operate a mouse.
- Color Contrast: Use sufficient color contrast to make text and interactive elements readable for users with visual impairments.
- Accessible Forms: Design forms that are easy to navigate and complete for users with different needs, such as those using screen readers or voice input.
- Seizure Safety: Do not design content that might trigger a seizure for people with photosensitive epilepsy
- Compatible : Maximize compatibility across devices and make sure content is compatible with assistive technologies
- Navigation : Provide multiple, intuitive ways for users to navigate content
- Input Assistance: Help users to avoid making mistakes; make corrections easy.
- Time: Provide user enough time to read and use content.
User Interface (UI):
- Simplify Navigation: Streamline the navigation to make it intuitive and easy for users to find what they need.
- Consistent Design: Maintain consistency in design elements such as buttons, fonts, and colors to create a cohesive UI.
- Visual Hierarchy: Use visual cues to prioritize content and guide users’ attention to the most important elements.
- Mobile Responsiveness: Ensure the UI is responsive and functions well on various devices and screen sizes.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Incorporate clear feedback for user interactions, such as button clicks or form submissions.
- Video Alternatives: provide alternatives for video and audio. Closed captions and audio descriptions are required for time-synced video.
- Text-Alternatives: Provide text alternatives for any non-text content so that it can be converted into other forms pople need.
User Experience (UX):
- User-Centric Design: Understand user behaviors and preferences to create an experience that meets their needs.
- Usability Testing: Conduct regular usability testing with actual users to identify pain points and areas for improvement.
- Personalization: Offer personalized experiences based on user preferences and behavior.
- Performance Optimization: Ensure fast loading times and smooth interactions to enhance the overall UX.
- Clear Call-to-Actions: Use clear and compelling call-to-action buttons to guide users through desired actions.
- Readable: Make text content easily readable and understandable, both visually and congnitively.
- Predictable: make pages appear and operate in predicatable ways.
- Adaptable: Create content that can be presented in different ways without losing information or structure.
- Clarity: Provide adequate color contrast and reduce visual clutter that affects legibility.
By implementing these strategies, you can create a more accessible, user-friendly, and engaging UI/UX, which can contribute to an increase in your user base.