Sesame Phone – A touch-free smartphone you can control by moving your head.

How does it Work?
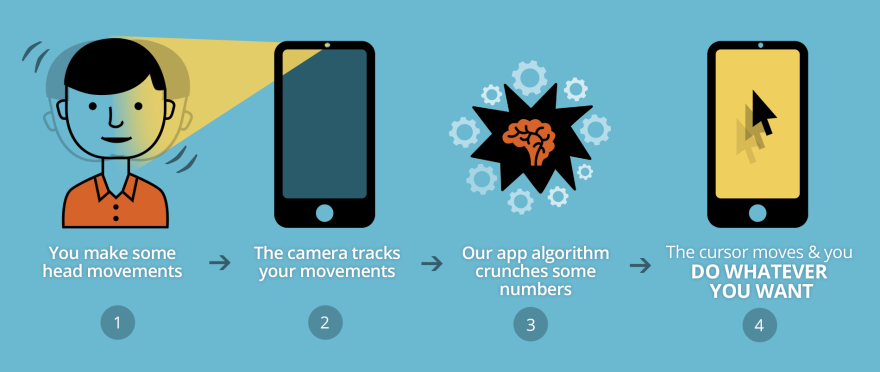
The Sesame phone works by tracking the user’s head movements using the built-in, front-facing camera on the phone. These tracked movements are combined with cutting-edge computer vision algorithms to create a cursor that appears on the screen of the phone, similar to a cursor you would see on a computer screen.
The on-screen cursor is controlled by the position and movements of a user’s head, and supports even minimal movements. You can operate any and all features of the device that you would normally operate using one finger on screen. Touch, swipe, browse, play, download, and more – it’s all possible using the Sesame smartphone.
Voice control is integrated to provide a truly hands-free experience for accessing the device. To turn the phone just say “Open Sesame” and it will wake up and start tracking you.
Sesame Enable Oris Phone Verizon Version 3
Features
- Touch-Free Control: Gesture recognition understands small head movements, eliminating the need for touch
- Integrated Voice Control : Use your voice to turn on/off the phone or switch between applications
- Works Out of the Box : Works touch-free immediately, no additional set-up required
- Lightweight Mobile Design : The Sesame smartphone uses Google Nexus 5 for the hardware
- Affordable & Elegant : No external hardware required
- Download Apps : Touch-free interface extends to nearly any app from the Google Play store
Sesame’s technology was made for people who have limited, or no use of their hands and are able to make small head movements.
Sesame’s goal is to offer a phone that works for the widest range of users, that represent a broad range of physical abilities. The Sesame Phone is highly customizable and works with very small head movement range.
- Spinal Cord Injuries (SCI)
- Cerebral Palsy (CP)
- Muscular Dystrophy
- Lou Gehrig’s Disease (ALS)
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Arthritis
Video Tutorial